Enhancing Judicial Impartiality in Ecuador: A Fuzzy Cognitive Map Approach Using Neutrosophic Logic and Fuzzification
Keywords:
Judicial impartiality, fuzzy cognitive maps, expert knowledge, Neutrosophic Logic fuzzificationAbstract
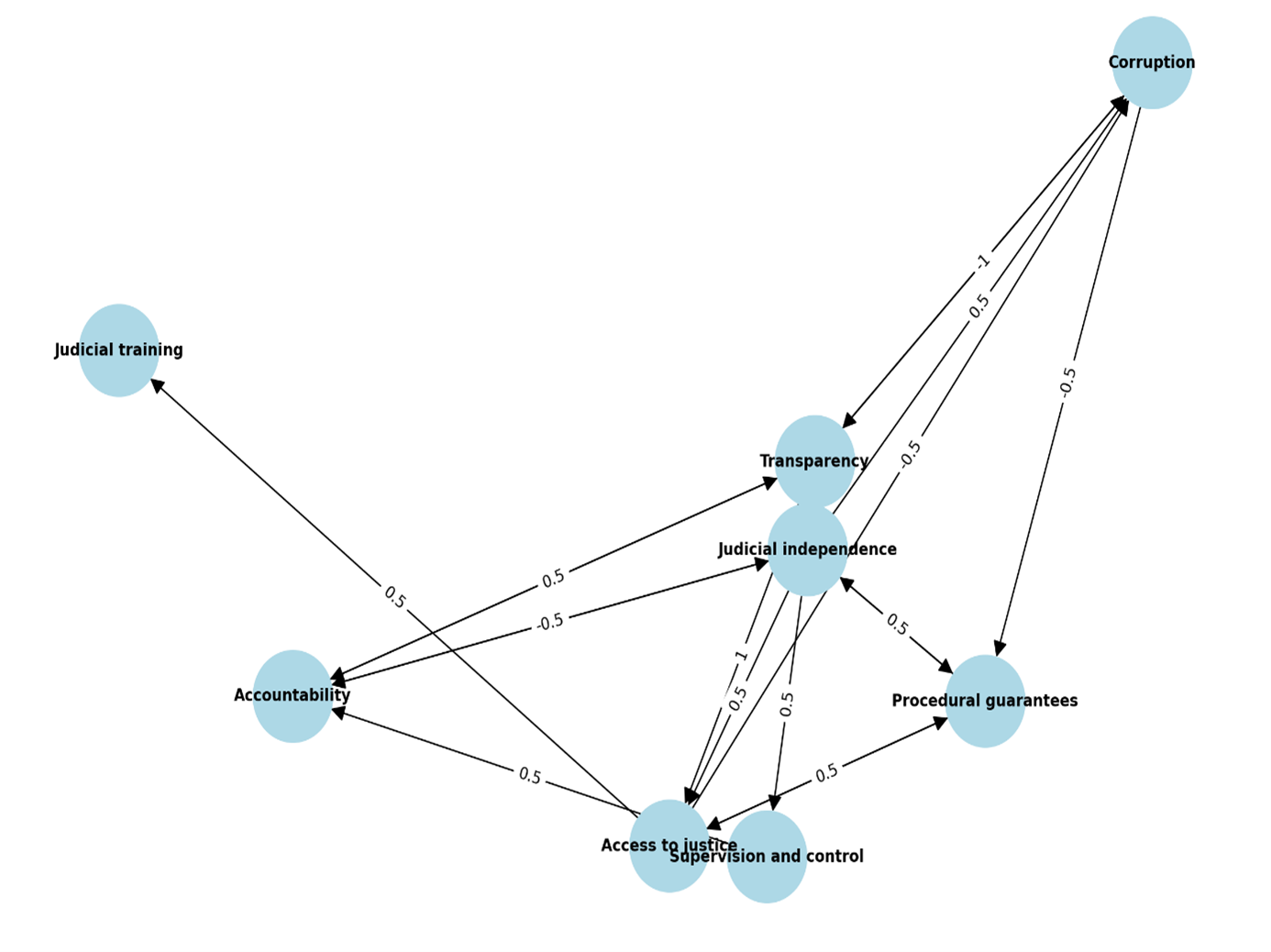
Fuzzy Cognitive Map (FCM) approach, with neutrosophic logic and fuzzification applied to assign weights to the relationships between key concepts. Through expert consensus, eight critical factors were identified: Judicial Independence, Transparency, Corruption, Judicial Training, Accountability, Access to Justice, Procedural Guarantees, and Supervision and Control. Centrality analysis revealed that Judicial Independence and Transparency are the most influential, while Judicial Training has the lowest impact. The use of neutrosophic logic and fuzzification allowed for a flexible and accurate representation of causal relationships, accounting for uncertainty within the system. The findings highlight the need for reforms focused on enhancing judicial independence and transparency, as well as addressing corruption and access to justice. Future research should incorporate dynamic simulations and machine learning to further improve predictive capabilities and deepen the understanding of policy impacts on judicial impartiality.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


