Neutrosophic Dynamic Network DEA: Efficient Allocation of Carryover Variables in Organizational Processes
Keywords:
Neutrosophic Set; Dynamic Network DEA; Decision Making; Carryover Variables.Abstract
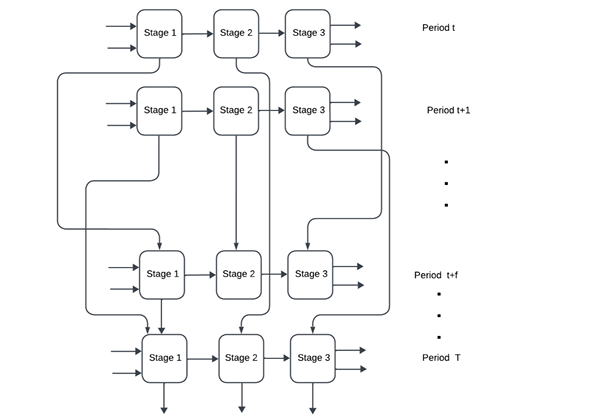
Carryover activities in dynamic DEA refer to the persistence of resources, inputs, or outputs across periods
in organizational processes, reflecting the impact of past decisions on current and future performance. In
practical applications, some carryover variables can extend beyond the immediate next period, and their
allocation is discretionary, controlled by the Decision-Maker (DM). This paper introduces a novel dynamic
network DEA (DNDEA) model aimed at optimizing the allocation of these carryovers and identifying
inefficiencies within a network system across multiple evaluation periods.
Recognizing the uncertainties present in real-world data, we incorporate neutrosophic sets to effectively
process uncertain information, which adds complexity to our analysis. To address this, we transform the
Neutrosophic Dynamic Network Slack-Based Measure (NDNSBM) model into a two-stage framework. By
leveraging the concept of Pareto efficiency, our model establishes boundaries for overall and period scores
across varying levels of truth, indeterminacy, and falsity. The key contribution of this work is the introduction
of discretionary carryover variables in DNDEA models, facilitating strategic allocation across future periods.
Additionally, the integration of neutrosophic data provides a more realistic approach to dynamic decision
making contexts. We validate our methodology through a numerical example evaluating the performance of
Iranian bank branches, demonstrating that our proposed model is more discriminative and offers deeper
insights into resource allocation strategies compared to the DNSBM model. This comprehensive approach
enhances understanding of resource management in dynamic environments, offering valuable implications for
decision-makers in various sectors.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







