Plithogenic Sets-Based MABAC Framework for Evaluating the Quality of Elderly Care Security Services for Left-Behind Elderly in Rural Areas of Western China: A Healthcare Industry Perspective
Keywords:
Elderly Care Security Services; Plithogenic Sets; Healthcare Industry; MABAC Framework; Left-Behind Elderly in Rural AreasAbstract
This study proposed a multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) methodology for
evaluating the elderly care security services. These services consist various criteria, so the
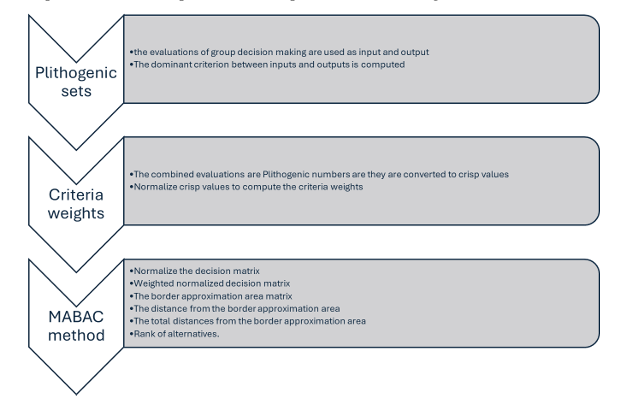
MCDM methodology is used. MABAC methodology is a MCDM method used to rank
the alternatives. The MABAC methodology is integrated under the plithogenic sets to
deal with vague and uncertainty data. The plithogenic sets are an extension of
neutrosophic sets to deal with inconsistencies data. The criteria weights are computed in
this study. Seven criteria and 13 alternatives are collected in this study. An application
with opinions of three experts evaluate the criteria and alternatives. The results show the
criterion Accessibility of Services has the highest weights and the criterion Technological
Integration in Care Services has the lowest weights. The sensitivity analysis is performed
to show the stability of rank of alternatives.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







