A Combined GIS-MCDM Approach to Site Selection of Temporary Shelter: A Case Study in Dahab, Egypt
Keywords:
Temporary shelter site selection; Disaster management; Geographic information system; CRITIC; T2NN.Abstract
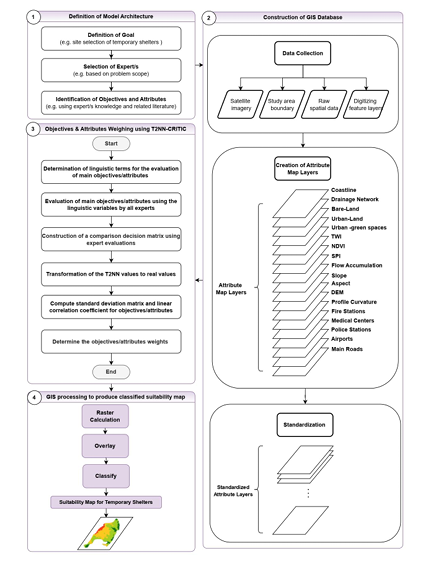
In this study, a model based on the Geographic Information System (GIS) and MCDM method: the
Criteria Importance through Inter-Criteria Correlation (CRITIC) based type-2 neutrosophic numbers
(T2NN) is used to give researchers and stakeholders a simple and reliable spatial decision-making tool.
First the model focuses on determining a group of experts with experience related to the study. The
selected group of experts then determines effective objectives and attributes concerning the study and
estimates the relative importance of each objective and its related set of attributes using a set of linguistic
variables. The T2NN-CRITIC method was used to evaluate the objectives and attribute weights and
importance. Second, the spatial attribute layers were integrated with the global weights evaluated using
ArcGIS Pro to rank and choose the most suitable site for the study. The proposed model was implemented
through a case study to select the most suitable site for temporary shelter in case of floods in Dahab,
Egypt. According to the analysis of the current study, 5.16% of the study area (17,550 Km2) is highly
suitable as a site for a temporary shelter in the event of a flood in Dahab, Egypt, (126,570 Km2) of the
study area classified as moderately suitable, (161,850 Km2) of the study area classified as marginally
suitable and, finally (34,080 Km2) classified as not suitable. Finally, sensitivity analysis has been used to
confirm the stability of the model results.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


