Neutrosophic Cognitive Maps for Clinical Decision Making in Mental Healthcare: A Federated Learning Approach
Keywords:
Federated Learning; Neutrosophic Cognitive Maps (NCMs); Mental Health; Psychological ConceptsAbstract
Due to data privacy concerns and a lack of broadly applicable modelling approaches,
mental health prediction encounters substantial challenges. This research introduces a pioneering
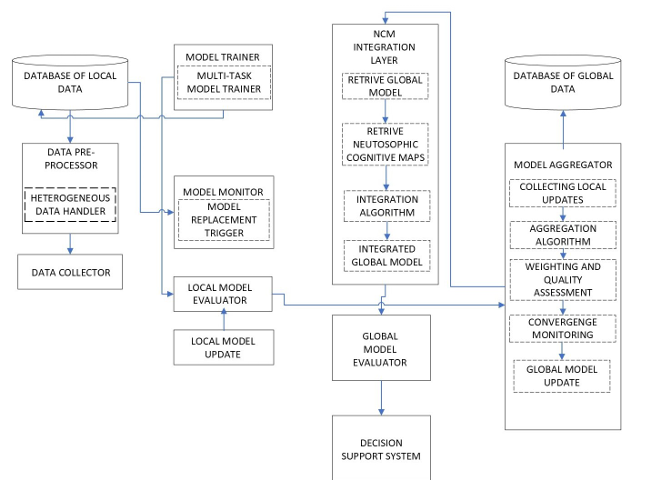
decentralized framework integrating federated learning with Neutrosophic Cognitive Maps
(NCMs) to facilitate secure and accurate mental health predictions while preserving data privacy.
This innovative approach allows collaborative NCMs training on sensitive patient data across
diverse sites without centralizing or transferring the data. The NCMs incorporated into the
framework effectively model relationships between various symptoms and mental health states,
offering interpretable insights into the complex dynamics of mental health. To address the
limitations of local data availability, a multi-task learning methodology is employed, leveraging
commonalities between related mental health prediction tasks to enhance modelling. Experiments
are done on a synthetic mental health dataset to validate the proposed approach, demonstrating
significant improvements. The decentralized nature of the approach ensures robust privacy
guarantees by preventing direct access to patient data. The proposed framework contributes to the
responsible application of soft computing and AI in the sensitive mental health domain.
Furthermore, the interpretability of NCM models facilitates a nuanced analysis of indeterminate
interrelationships between various psychological concepts, offering valuable support for
data-driven decision-making in mental health contexts.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







