Application of neutrosophic fuzzy logic in the assessment of risk factors for type II diabetes
Main Article Content
Abstract
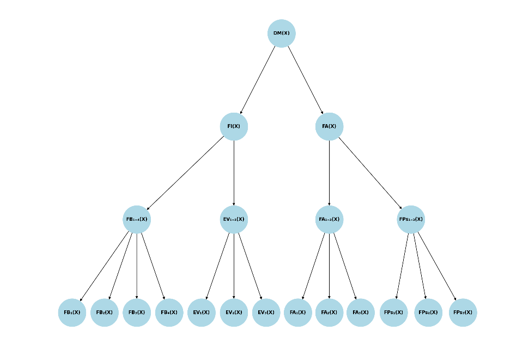
A research study was conducted with the purpose of analyzing the prevalence of type II diabetes mellitus in older adults, identifying its main risk factors through a systematic literature review and the application of compensatory fuzzy logic with neutrosophic numbers. The review included scientific articles published between 2018 and 2023, selected using the PRISMA methodology from databases such as PubMed, Scopus, SciELO, and Google Scholar. Subsequently, the most relevant risk factors were linguistically evaluated and processed using neutrosophic fuzzy logic tools to obtain representative truth values. Among the most prominent findings, influential factors included unhealthy diet, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, and advanced age. External variables such as social isolation and limited access to healthcare services and safe spaces for physical activity were also considered. The fuzzy logic analysis allowed for a more accurate representation of the uncertainty inherent in expert judgments by integrating linguistic scales with neutrosophic numerical values. It was concluded that type II diabetes in older adults poses an increasing threat to healthcare systems due to its high prevalence and multiple interrelated factors. The application of tools based on neutrosophic fuzzy logic proved to be useful in supporting diagnosis and clinical decision-making, especially in contexts with incomplete or ambiguous information. Strengthening preventive and personalized strategies that take into account both individual and contextual factors was recommended.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.