Neutrosophic Topological Spaces for Spatially-Aware Uncertainty Modeling in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Keywords:
Neutrosophic Logic; Neutrosophic Topological Spaces; Lung Cancer Detection; Medical Uncertainty Modeling; Chest X-ray Analysis; Diagnostic Ambiguity; Spatial Reasoning; Indeterminacy Modeling; Topological Operators; Explainable Medical AI.Abstract
Diagnostic uncertainty in chest X-rays particularly for early-stage lung cancer
arises from overlapping radiographic features and indeterminate boundaries. While
neutrosophic logic effectively represents ambiguity through truth (T), indeterminacy (I), and
falsity (F) sets, its inability to encode spatial relationships among uncertain regions limits its
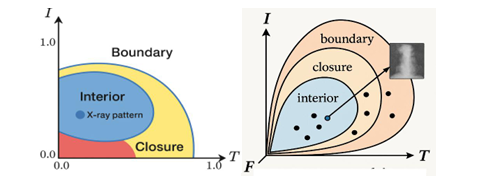
clinical utility. To address this, we develop neutrosophic topological spaces (NTS), where
topological operators (interior, closure, boundary) act on T, I, and F components
independently. This allows:
1. Spatial reasoning: Quantification of transitional zones (e.g., between tumor and
parenchyma) via boundary operators.
2. Structured ambiguity: Hierarchical clustering of indeterminate regions based on
connectivity.
Evaluated on the ChestX-ray8 dataset, NTS achieves 90% accuracy (vs. 81% for
conventional neutrosophic classifiers), with a 15% reduction in false positives for sub
centimeter nodules. Crucially, the model’s topological constraints enable radiologist
aligned interpretability, as demonstrated by a 0.82 inter-rater agreement score (Cohen’s κ)
in a clinician study. By fusing spatial semantics with neutrosophic uncertainty, NTS provides
a path toward actionable diagnostics in low-certainty scenarios.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


