Neutrosophic Hypothesis to Validate the Efficacy and Safety of Propolis in the Treatment of External Bacterial Otitis in Canines
Keywords:
propolis, external bacterial otitis, domestic canines, neutrosophic hypothesisAbstract
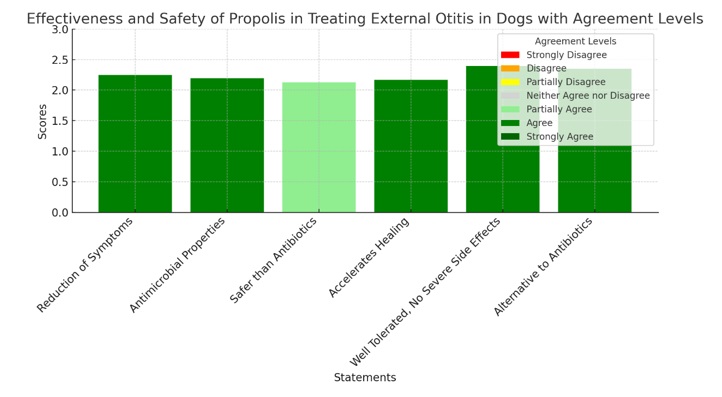
Propolis, known for its antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, antiviral, immunomodulatory, and anti-parasitic properties, has been the subject of this study to evaluate its efficacy and safety in the treatment of bacterial external otitis in domestic canines. Through questionnaires administered to veterinary experts and the use of neutrosophic logic for hypothesis testing, perceptions based on clinical experiences and scientific literature were analyzed. The results indicate strong agreement that propolis is effective and safe, surpassing some aspects of conventional antibiotic treatments and demonstrating high tolerability without serious side effects. This acceptance underscores its potential as a natural alternative in veterinary treatments, particularly valuable in cases of antimicrobial resistance or allergies to traditional medications. This study provides significant evidence supporting the integration of propolis into veterinary practices, suggesting the need for further research and possible revisions of current clinical practices for managing bacterial conditions in animals. The use of neutrosophic hypotheses facilitated a more detailed and deeply informed interpretation of the level of expert agreement on the properties of propolis in the condition analyzed.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


