Combining Two Auxiliary Variables for Elevated Estimation of Finite Population Mean under Neutrosophic Framework
Keywords:
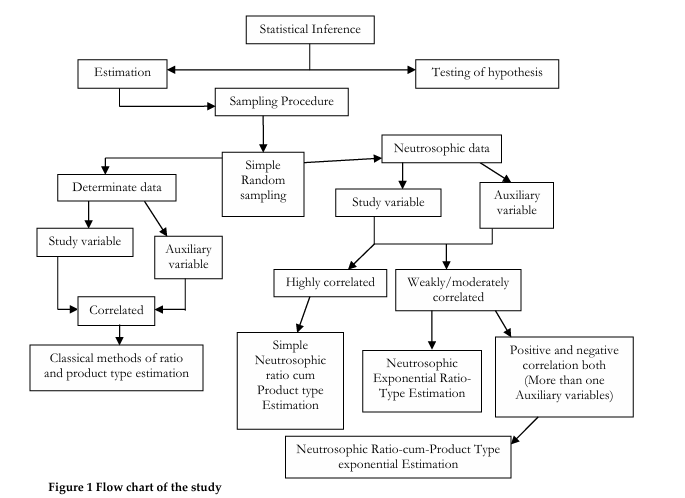
Neutrosophic Ratio-cum-Product exponential type estimator; Bias; Mean square error; Neutrosophic Simulation; Percentage relative efficiency.Abstract
Typically, most researchers rely on precise data for estimating population parameters using
classical statistical methods. However, there are scenarios where dealing with uncertain and imprecise
data in the form of intervals becomes necessary. To tackle this challenge, various adaptations of classical
estimators, such as the neutrosophic ratio estimator and their improved ones, have emerged. This article
introduces a novel estimator known as the neutrosophic ratio-cum-product exponential estimator
combining two auxiliary variables, specifically designed for the elevated estimation of population mean
in such situations. Performance evaluation is conducted using metrics like Mean Square Error (MSE) and
Percentage Relative Efficiency (PRE). The effectiveness of the proposed estimator is demonstrated
through both empirical and simulation studies. Additionally, its practical applicability is showcased using
agricultural data. The results illustrate that the proposed estimator surpasses all other estimators
discussed in this paper. To justify the usefulness of neutrosophic estimators over their classical ones, a
simulation study is also made. Simulation results obtained for classical estimators have also been
compared with their neutrosophic adaptations.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


