Predicting Student Behavior Using a Neutrosophic Deep Learning Model
Keywords:
System Development Life Cycle, Deep Neural Network, Deep learning, Educational Data Mining, Neutrosophic Sets, Indeterminacy in Data.Abstract
We developed an information system using an object-oriented programming language
and a distributed database (DDB) consisting of multiple interconnected databases across a computer
network, managed by a distributed database management system (DDBMS) for easy access. An
intelligent system was designed to assess the difficulty level of preliminary exams and select
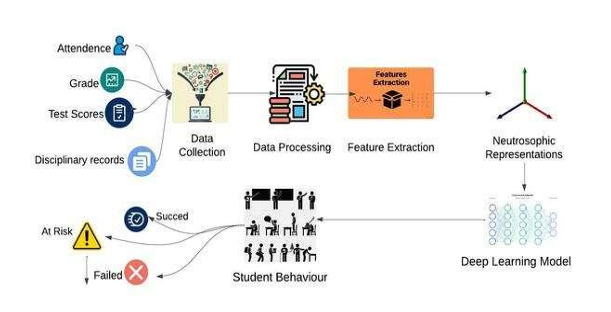
top-performing advanced students using a Neutrosophic Deep Learning Model. The dataset was
randomly split into training (80%) and testing (20%) sets, and the model, trained with the Adam
optimizer at a 0.001 learning rate over 50 epochs, incorporated early stopping based on validation
loss. This system, implemented at a traditional Egyptian university, achieved a 95% accuracy in
predicting student dropout. Student behavior, influenced by personal, environmental, and
academic factors, is often evaluated subjectively, leading to inconsistent results. Traditional machine
learning approaches struggle with the inherent uncertainty in behavioral data. To address this, we
combined neutrosophic theory—a mathematical framework that accounts for truth, falsity, and
indeterminacy—with deep learning, which excels at learning complex data relationships, to predict
student outcomes such as dropout rates. Evaluating the model on student data, including
attendance and grades, showed superior accuracy, achieving a determination coefficient of 0.95,
demonstrating the approach's potential for identifying at-risk students and enabling targeted
interventions.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






