Detection of Cardiovascular Diseases Using Predictive Models Based on Deep Learning Techniques: A Hybrid Neutrosophic AHP-TOPSIS Approach for Model Selection
Keywords:
Heart Disease, Prediction, Convolutional Neural Network, Deep Neural Network, Multilayer Perceptron, Neutrosophic AHP-TOPSISAbstract
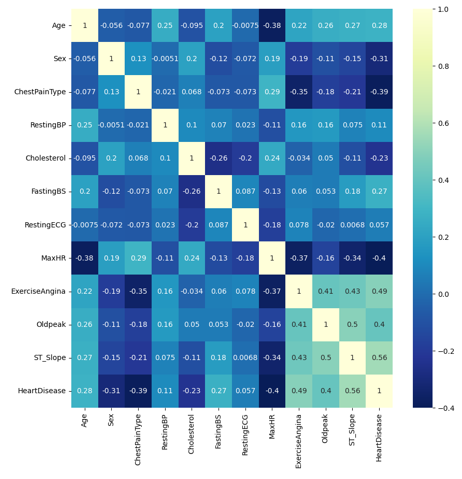
In Ecuador and globally, cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of mortality, accounting for a worrying 26.49% of deaths in 2019. An approach based on deep learning is applied to improve the capacity for early prediction and reduce its incidence. In this work, three different models were proposed and compared: deep neural networks (DNN), convolutional neural networks (CNN), and multilayer perceptron (MLP). Experiments were conducted in two scenarios: one using a dataset that included 12 variables, and another in which the variables were reduced to those most significantly correlated with cardiovascular disease, i.e., 4 variables; both scenarios with 918 clinical records per variable. Using the Neutrosophic AHP-TOPSIS method for model selection, the CNN model trained with the original dataset was identified as the best-performing model among the proposed options. In specific terms, the evaluation metrics of the CNN model were as follows: an accuracy of 92.17%, a sensitivity of 94.51%, a specificity of 90.78%, an F1-Score of 93.30%, and an area under the ROC curve of 90.03%.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


