A new method for measuring the effectiveness of teacher evaluation instruments in improving pedagogical performance in higher education based on the neutrosophic 2-tuple linguistic model and offset logic
Keywords:
Educational Quality, Higher Education, pedagogical evaluation, pedagogical performance, Computing with Words (CWW), neutrosophic 2-tuple linguistic model, offsets, offset logicAbstract
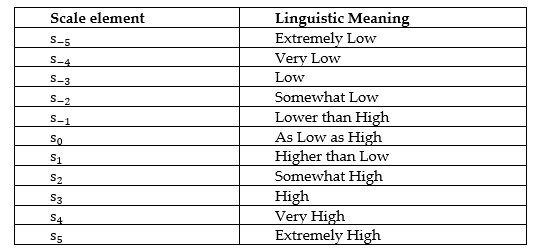
Assessment in a teaching-learning process allows teachers to determine to what degree students are assimilating the content and are meeting the objectives of the study program. That is why when there are fine-tuned assessment instruments, it is assumed that there is better pedagogical performance. This is a consequence of the fact that the accuracy of the tests allows better adjustment of the classroom methods carried out by the teacher. In this article, we propose a technique that allows determining the degree of effectiveness of assessment instruments on school results and their relationship with pedagogical performance. We focus specifically on higher education in Ecuador, although the method may be valid in another context. For the design of the method, we took into account that the teacher or the specialist who evaluates is better understood with the help of a linguistic measurement scale. In addition, experience shows that in each evaluation there is indeterminacy and uncertainty. That is why the proposed method is based on the neutrosophic 2-tuple linguistic model. This is a model of Computing with Words, where they are evaluated with a natural language scale and the indeterminacy of the evaluation is also taken into account. On the other hand, offsets allow obtaining logical results between these words when logical operations are performed between their indices that are outside the classic truth values in [0, 1].
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






