Study of the impact of emerging technologies on the conservation of protective forests through the plithogenic hy-pothesis and neutrosophic stance detection
Keywords:
Plithogenic Hypothesis, Neutrosophic Stance Detection, Emerging Technologies, Forest Conservation, Threat Detection, Biodiversity Monitoring, Community Participation, SustainabilityAbstract
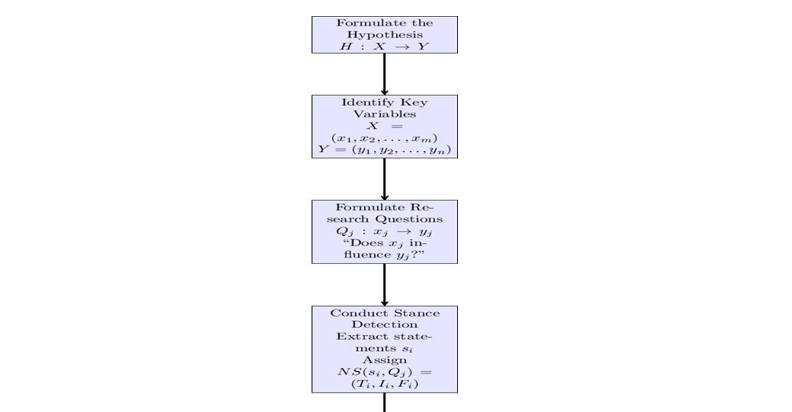
This paper investigates the efficacy of emerging technologies in protective forest conservation—artificial intelligence, drones, remote sensing, and blockchain—and whether such tools foster threat detection and enhanced biodiversity and human interaction. As deforestation and climate change continue to plague the planet, protected areas become more critical, and although successful conservation efforts exist, traditional tools fail to adequately provide the granularity and scalability required for nuanced action such as illegal logging or forest fires. The emerging abilities of these innovations have been published in scientific literature. However, there exists a translational gap in a systematic determination of their efficacy since levels of uncertainty and constraints are discussed upon implementation across varying ecological and socioeconomic spectrums. Therefore, this paper seeks to fill the void utilizing the plithogenic hypothesis—a neutrosophic application of modeling uncertainty through the probability of truth, indeterminacy, and falsity. 125 articles were examined for feasibility with the use of the Consensus Meter. Results denote a 48% probability of actualness that such technologies do work—74.3% that they increasingly foster early detection of threats, 72% that they help monitor biodiversity; yet 32% indeterminacy suggests challenges to success including expense and absent infrastructure. This is a unique form of assessment of efficacy in uncertain, complicated environments. Ultimately, implementation suggestions can include need vs. idea vs. environmental implementation and feasibility of financing and community support/inclusivity to realize what would theoretically contribute to forest conservation and policy proposals that use emerging technologies yet acknowledge ecological and socioeconomic realities.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






