Computational intelligence for disease diagnosis: an approach based on neutrosophic logic
Keywords:
Neutrosophic logic; uncertainty; medical diagnosis.Abstract
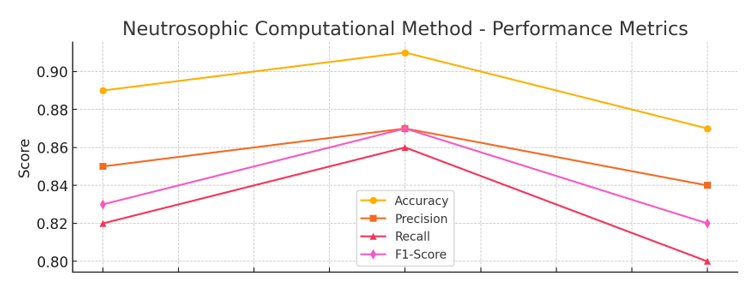
Medical diagnosis faces significant challenges due to the inherent uncertainty and ambiguity of clinical data. In this context, this paper proposes a neutrosophic logic-based approach to disease diagnosis, with an emphasis on the detection of chronic kidney disease. The primary objective was to develop a computational method that adequately represents and manages uncertainty by transforming clinical attributes into neutrosophic structures composed of triplets (T: truth, I: indeterminacy, F: falsity). The implemented methodology included the collection and preprocessing of real clinical data extracted from the UCI repository (135 patients), the application of imputation and normalization techniques, the definition of diagnostic criteria, the fuzzification of attributes using membership functions (triangular, trapezoidal, Gaussian, and sigmoid), and the application of neutrosophic logic to obtain a final diagnosis. The proposal was evaluated using standard metrics such as accuracy, precision, sensitivity, F1-score, MAE, and RMSE. The results obtained from experimental tests show that the model achieves accuracy levels above 90%, with a low margin of error, which validates its ability to offer reliable diagnoses even in the presence of ambiguous or incomplete data. It is concluded that the neutrosophic approach constitutes an effective and flexible alternative to traditional binary classification models, providing a robust computational framework for medical decision-making under uncertainty.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






