Neutrosophic State Learning for High-Stakes Systems Using a Dynamic Triplet Model of Support Contradiction and Uncertainty
Keywords:
Neutrosophic modeling; machine learning under uncertainty; temporal state estimation; indeterminacy quantification; multi-hypothesis clinical monitoring; dynamic truth indeterminacy–falsity triplet.Abstract
Machine learning models are increasingly used in high-stakes settings such as critical
care, energy management, and environmental monitoring. These settings are difficult because the
available data can be incomplete, delayed, low quality, or internally contradictory. Standard
models still tend to return a single prediction or a single confidence score, even when the situation
is not actually settled. This creates false certainty and can lead to unsafe actions.
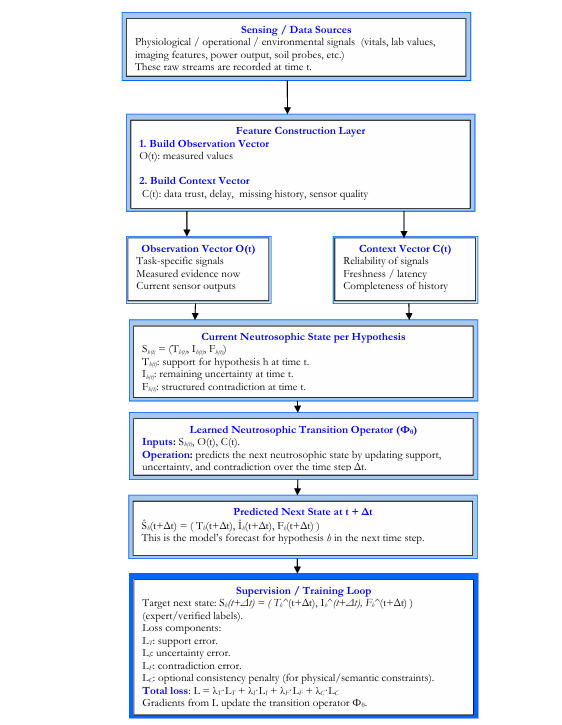
We introduce a framework called Neutrosophic Machine Learning State Modeling (NMLSM). In
this framework, the system does not describe each hypothesis with one number. Instead, it learns
three separate quantities for every hypothesis at every point in time: (i) how much current evidence
supports it, (ii) how much current evidence contradicts it, and (iii) how much uncertainty remains
because the information is missing, unreliable, or ambiguous. These three quantities are learned
independently and are allowed to coexist. For example, the model is allowed to say that a
hypothesis is both supported and challenged at the same time, and also admit that part of the
situation is still unresolved. This reflects real conditions, rather than forcing a premature decision.
The framework also models how these three quantities evolve as new information arrives. It uses
both raw observations (what was measured) and context (how trustworthy those measurements
are). In training, the model is supervised not only on how well it can recognize supporting
evidence, but also on how well it can recognize contradictory evidence and how honestly it can
represent remaining uncertainty.
We demonstrate the approach in an intensive-care scenario by tracking two possible diagnoses for
the same patient in parallel. Instead of collapsing to a single “most likely” diagnosis too early, the
model maintains a transparent view of support, doubt, and refutation for each diagnosis as the
case unfolds. This capability is important in situations where taking the wrong action too
confidently can be more dangerous than admitting that the system is not yet sure.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Neutrosophic Sets and Systems

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


